Torque sensors are essential components in the operation of many industrial and technical systems. They measure and record torque, or rotational force, on gearboxes, crankshafts, engines, and other rotating elements. This data allows engineers to understand how these systems work under different conditions and identify potential problems before they become serious issues.
This article will look at the fundamentals of torque sensors—what they are, how they work, their advantages over traditional methods of measurement—and their various applications in industry. We’ll also take a closer look at some examples of how they can be used in real-world scenarios.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is a Torque Sensor?

A Torque Sensor, known as a torque transducer or torque meter, is a device used to measure and record the torque on various rotating systems such as gearboxes, crankshafts, rotors, and engines. They help detect the perception of torque on a variety of rotating or non-rotating mechanical components. They convert a torsional mechanical input into an electrical output signal, enabling precise measurement of the amount of Torque applied to an object.
In addition to industrial applications, they are found in electronic devices like electric bikes. In this context, it measures the rider’s pedaling force to determine the amount of electric power to apply to the bike. The harder you pedal, the more power it gives, making these adjustments in real time.
In automotive applications, the torque sensor in the electric power steering system measures the Torque the driver applies to the steering wheel. Based on this data, the electronic control unit calculates the steering assistance that the electric motor needs to apply.
Different Types of Torque Sensors
They come in various types, each designed to serve a specific application or environment. Here are some of the most common types of torque sensors:
- Rotary Torque Sensors: These sensors measure the Torque on a rotating component. They are often used in engine and transmission, dynamometers, and electric motor testing.
- Reaction Torque Sensors: These sensors measure static Torque or Torque that is not causing any rotation. They are commonly used for mixer, engine mount, and gearbox testing.
- Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) Torque Sensors: This type of sensor uses a wave of ultrasonic sound passed over a crystalline material to measure Torque. The wave’s speed changes depending on the applied Torque, which is then measured.
- Optical Torque Sensors: These sensors use light to measure Torque. A beam of light is sent through a fiber optic cable wrapped around the shaft. The light’s polarization changes as the shaft twists, which can be measured and converted into a torque reading.
- Strain Gauge Torque Sensors: Strain gauge sensors measure an object’s deformation (strain) when Torque is applied. The strain gauge is bonded onto the shaft, and as the shaft twists under Torque, the resistance of the strain gauge changes. This change in resistance can be measured and used to determine the Torque.
- Magnetoelastic Torque Sensors: These sensors work on the principle that a material’s magnetic properties change when Torque is applied. They are well-suited for environments with high temperatures and pressures.
Each type of torque sensor has unique features and benefits, and the choice of which one to use will depend on the application’s specific requirements.
Advantages of Torque Sensors

They provide several advantages across numerous applications, from automotive testing to industrial automation. Here are some of the key advantages of using them:
Precision
They are known for their high accuracy and precision. They can measure minute changes in Torque, often within a fraction of the total measurement range. This high degree of accuracy is crucial in fields such as automotive testing, where small differences in Torque can significantly impact performance and safety. Similarly, precise torque measurements can ensure the consistent performance of products and machinery in manufacturing and quality control processes.
Versatility
They come in various types, each designed to serve specific applications or environments. For instance, rotary torque sensors are ideal for measuring the Torque on rotating components such as engines and transmissions. In contrast, reaction torque sensors are perfect for measuring static Torque in mixers or engine mounts. This versatility makes them applicable across a wide range of industries, from automotive to industrial automation, aerospace, energy, and more.
Durability and Quality
They are built to last. They are designed to be robust and resistant to wear and tear, making them suitable for use in harsh industrial environments where they may be exposed to elements like dust, heat, cold, or moisture. Their durability ensures reliable performance over time, minimizing the need for replacements and reducing maintenance costs.
Real-time Data
One of the key advantages of torque sensors is their ability to provide real-time torque measurements. This means that as soon as Torque is applied to a system, the sensor can immediately detect and report this information. Real-time data is vital for systems that require immediate adjustments or controls based on torque measurements, such as in robotics or automated manufacturing processes.
Improved Efficiency and Safety
By providing accurate torque measurements, they can help optimize the performance and efficiency of machines and systems. For example, in an electric power steering system, the torque sensor measures the Torque the driver applies to the steering wheel, and based on this data, the electronic control unit calculates the steering assistance that the electric motor needs to apply. This improves the vehicle’s efficiency and enhances safety by providing appropriate steering assistance based on the driver’s input.
Industrial Applications of Torque Sensors
Torque sensors play a vital role in various industrial applications. They are instrumental in ensuring accuracy, efficiency, and safety in different processes. Here are some of the key industrial applications of torque sensors:
- Manufacturing and Production: Torque sensors are used in automated manufacturing processes to ensure that machines are working within their specified torque ranges. This helps maintain product quality and prevent equipment damage. They are also used to monitor and control the Torque in fastening processes.
- Automotive Industry: In the automotive industry, torque sensors are used in power steering systems, engine testing, transmission testing, and electric motor testing. They help enhance vehicle performance and safety.
- Aerospace: Torque sensors are used to test and develop aircraft engines and components. They help ensure that these parts meet the rigorous standards for safe and efficient operation.
- Energy Industry: In wind turbines, they are used to measure the Torque on the turbine shaft, helping to optimize energy production and prevent damage to the turbine.
- Robotics: In robotics, they give robots a sense of touch or ‘feel.’ They help robots apply the right force when interacting with objects, which is crucial in assembly or handling delicate items.
- Material Testing: Torque sensors are used in material testing to measure the torsional strength of various materials. This data is critical in determining the suitability of a material for specific applications.
- Medical Industry: In the medical field, they are used in various devices, such as surgical robots, where they provide feedback to control the Torque applied during surgical procedures.
These are just a few examples; torque sensors’ versatility means they can be used in many more applications across different industries.
How To Use Torque Sensors?
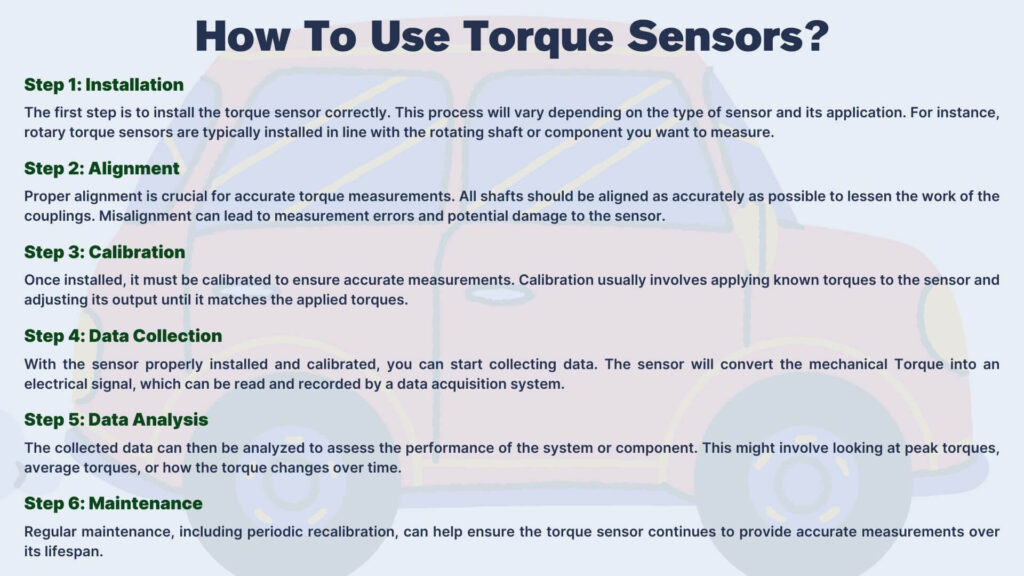
Using a torque sensor involves several steps, from installation to calibration. Here’s a general guide on how to use them:
Step 1: Installation
The first step is to install the torque sensor correctly. This process will vary depending on the type of sensor and its application. For instance, rotary torque sensors are typically installed in line with the rotating shaft or component you want to measure. Reaction torque sensors, on the other hand, are installed in line with a static object that’s generating or being acted on by Torque.
Step 2: Alignment
Proper alignment is crucial for accurate torque measurements. All shafts should be aligned as accurately as possible to lessen the work of the couplings. Misalignment can lead to measurement errors and potential damage to the sensor.
Step 3: Calibration
Once installed, it must be calibrated to ensure accurate measurements. Calibration usually involves applying known torques to the sensor and adjusting its output until it matches the applied torques.
Step 4: Data Collection
With the sensor properly installed and calibrated, you can start collecting data. The sensor will convert the mechanical Torque into an electrical signal, which can be read and recorded by a data acquisition system.
Step 5: Data Analysis
The collected data can then be analyzed to assess the performance of the system or component. This might involve looking at peak torques, average torques, or how the torque changes over time.
Step 6: Maintenance
Regular maintenance, including periodic recalibration, can help ensure the torque sensor continues to provide accurate measurements over its lifespan.
Remember, always refer to the specific user manual or guide provided by your particular torque sensor manufacturer for detailed instructions tailored to your specific model and application.
Streamline Torque Measurements Using a Low-code Platform
If you manage a business that requires precise torque measurement, using a reliable digital torque wrench can enhance accuracy and efficiency. Digital torque wrenches provide consistent and precise torque readings, reducing human error and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
DataMyte’s LightStar™ Torque Wrench is designed to deliver highly accurate torque measurements with digital precision. This tool allows you to monitor, record, and analyze torque data seamlessly, improving quality control and reducing variability in your processes. With real-time data capture and storage, you can easily track torque performance over time for compliance and optimization.
Additionally, DataMyte’s torque solutions integrate with quality management systems, allowing for automated data collection and analysis. This ensures that your torque measurements are not only precise but also documented for audits and process improvements.
With DataMyte’s Torque Wrench, you get an all-in-one solution for accurate, efficient, and traceable torque measurement. Book a demo today to see how DataMyte can help streamline your torque measurement process.
Conclusion
Gone are the days of relying on manual methods and guesswork to measure Torque. Torque sensors are reliable, accurate devices that measure the varying forces applied to rotating systems. With a low-code platform like DATAMYTE, you can quickly and easily customize your torque measurement system according to your specific requirements. Get started today!



